How to Calculate Sewing Thread Consumption in Apparel Industry
How to Calculate Sewing Thread Consumption in the Apparel Industry?
Sewing Thread Calculation Method in the Apparel Sector:
Sewing thread consumption calculation is one of the most important factors in apparel merchandising. An apparel merchandiser must have accurate knowledge about the sewing thread consumption process. Otherwise, the sewing thread will be short during apparel production. In another two articles, I have shared Sewing Thread Consumption for Different Stitches and Sewing Thread Consumption for Different Apparel. Now, I have presented here the sewing thread calculation method that describes How to Calculate Sewing Thread Consumption in the Apparel Industry.
Sewing Thread Consumption Calculation Method in the Apparel Sector:
In the apparel manufacturing industry, sewing thread can be calculated by following four methods. Those are in the below:
- Stitch and unravel method.
- Stitch and measure method,
- Arithmetic method,
- Using software programs.
To calculate Sewing Thread Consumption, All the above methods are explained in the following:
1. Stitch and Unravel Method:
In this method, at first the fabric is first sewn up to a standard length say for 10cm or 20cm. then the stitched sewing thread is unraveled fully and then the length of the sewing thread is measured. This is a more time-consuming method.
For example, if for 10cm of stitch length, after unraveling the sewing thread length is 1 meter, then the sewing thread consumption is 1 meter per 10cm or 10cm per cm of stitch length.
2. Stitch and Measure Method:
In case of this method, a standard length of sewing thread is taken or marked; say, for example, 5 meters or 10 meters. Then it is sewn fully till the sewing thread is finished or the mark is reached in the sewing needle. Now, measure the length of the stitch length. This is one of the easiest methods of sewing thread calculation.
For example, for 10 meters of sewing thread, if the stitch length is 1 meter then the sewing thread consumption is 10 meters per meter of stitch length or 1 meter per 10cm of stitch length,h or 10cm per cm of stitch length.
3. Arithmetical Method:
In this method, sewing thread requirement may be calculated using parameters like stitch length, stitch width, stitch depth or height and stitches per inch or cm. Sewing thread consumption,
= {(Stitch length + stitch width + stitch depth) × stitch per inch or cm}
However, this method is difficult for stitches where multiple sewing threads are used.
4. Using Software Programme:
There are sewing thread software programs namely “sewing thread inventory planner” is used to calculate the sewing thread requirement in an effective way. Sewing thread requirements can be quickly and easily can be calculated from a folder without much effort For the most important product groups in men’s and boys’ wear and ladies’ wear. This program is built on the basis of illustrations of models and model elements and their respective sewing thread requirements.
This program will consider all the important parameters that influence the sewing thread consumption, and create an exact sewing thread consumption calculation per sewing operation.
All one needs to do is just enter the required seam positions that are to be calculated and the respective parameters. The calculation and exact calculation is done by the software.
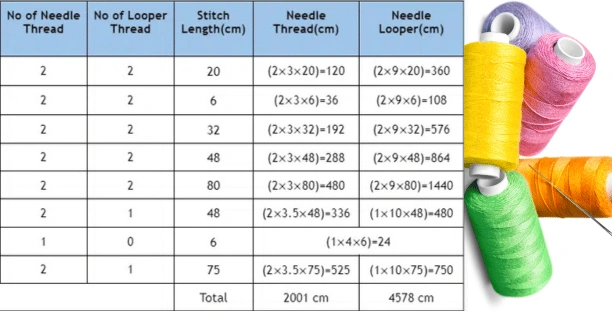
Machine Wise Sewing Thread Consumption in the Apparel Industry:
Sewing thread is one of the most important trimmings for apparel. Apparel merchandiser has to calculate sewing thread consumption before starting the apparel production. Sewing thread consumption is not an easy task, especially for the newcomers of this sector. If an apparel merchandiser gets a sewing thread consumption chart including stitch type consumption then his total work will be very easy to complete sewing thread consumption. As its importance, this article has presented a table which contains sewing consumption according to types of stitch and sewing machine.
Sewing Thread Consumption for Different Sewing Machines and Stitches:
The approximate sewing thread requirements for various stitch types are given below:
(Here, NT= Needle Thread, BT= Bobbin or Looper Thread, CT= Cover Thread)
| SL No. | Stitch Type | Seam width (mm) | Stitch per cm | Thread requirement per 1m of seam | % |
| 01 | Single- thread chain stitch (101) | – | 2 | NT: 3.80m | 100% |
| 02 | Single-thread blind stitch (103) | – | 2 | NT: 4.50m | 100% |
| 03 | Single-thread blind stitch (105) | – | 2 | NT: 4.50m | 100% |
| 04 | Long stitch (205)Hand stitch | – | 4 | NT: 1.40m | 100% |
| 05 | Double lock stitch (301) | – | 4 | NT: 1.40m | 50% |
| BT: 1.40m | 50% | ||||
| 2.80m | |||||
| 06 | Double lock stitchzigzag (304) | 5 | 4 | NT: 2.70m | 50% |
| BT: 2.70m | 50% | ||||
| 5.40m | |||||
| 07 | Double lock stitchMulti stitchzigzag (304) | 8 | 8 | NT: 6.50m | 50% |
| BT: 6.50m | 50% | ||||
| 13m | |||||
| 08 | Double chain stitch (401) | – | 4 | NT: 1.50m | 35% |
| BT: 2.80m | 65% | ||||
| 4.30m | |||||
| 09 | Double chain stitch zigzag (401) | 3 | 4 | NT: 2.40m | 35% |
| BT: 4.40m | 65% | ||||
| 6.80m | |||||
| 10 | Two-needle double chain stitch (406) | 5 | 4 | NT: 3.40m | 29% |
| BT: 8.40m | 71% | ||||
| 11.80m | |||||
| 11 | Three-needle double chain stitch (407) | 6 | 4 | NT: 5.10m | 30% |
| BT: 11.60m | 70% | ||||
| 16.70m | |||||
| 12 | Two times double chain stitch (408) | 6 | 4 | NT: 3.40m | 22% |
| BT: 6.20m | 40% | ||||
| CT: 5.80m | 38% | ||||
| 15.40m | |||||
| 13 | Single-thread over edge stitch (501) | 7 | 4 | NT: 16.40m | 100% |
| 14 | Two-thread over edge stitch (502) | 14 | 4 | NT: 1.70m | 15% |
| BT: 10.00m | 85% | ||||
| 11.70m | |||||
| 15 | Two-thread over edge stitch (503) | 5 | 4 | NT: 6.70m | 57% |
| BT: 5.00m | 43% | ||||
| 11.70m | |||||
| 16 | Three-thread over edge stitch (504) | 5 | 4 | NT: 1.70m | 12% |
| BT: 12.10m | 88% | ||||
| 13.80m | |||||
| 17 | Three-thread over edge stitch (505) | 5 | 4 | NT: 6.30m | 46% |
| BT: 7.50m | 54% | ||||
| 13.80m | |||||
| 18 | Four-thread over edge stitch (512) | 6 | 4 | NT: 3.40m | 21% |
| BT: 12.90m | 79% | ||||
| 16.30m | |||||
| 19 | Four-thread over edge stitch (514) | 6 | 4 | NT: 3.40m | 20% |
| BT: 13.70m | 80% | ||||
| 17.10m | |||||
| 20 | Two needle covering chain stitch (605) | 6 | 4 | NT: 3.40m | 205 |
| BT: 8.40m | 50% | ||||
| CT: 5.10m | 30% | ||||
| 16.90m | |||||
| 21 | Three needle covering chain stitch (605) | 6 | 4 | NT: 5.10m | 23% |
| BT: 11.60m | 52% | ||||
| CT: 5.80m | 25% | ||||
| 16.90m | |||||
| 22 | Four needle covering chain stitch (607) | 6 | 4 | NT: 6.80m | 25% |
| BT: 14.80m | 54% | ||||
| CT: 5.80m | 21% | ||||
| 27.40m | |||||
| 23 | Circular tack single-thread chain stitch-zigzag (107) | 2 | 7 | NT: 0.07m | 100% |
| 24 | Bar tack-double lock stich – zigzag (304) | 12 | 42 | NT: 0.30m | 60% |
| BT: 0.20m | 40% | ||||
| 0.50m | |||||
| 25 | Lingerie button hole single thread, chain stitch- zigzag (107) | 16 | 90 | NT: 0.50m | 100% |
| 26 | Lingerie button hole double lock stitch- zigzag (304) | 18 | 160 | NT: 0.10m | 10% |
| BT: 0.85m | 90% | ||||
| 0.95m | |||||
| 27 | Eyelet button hole without bar tack, double chain stitch, zigzag (404) | 30 | 85 | NT: 0.80m | 80% |
| BT: 0.20m | 20% | ||||
| 1.00m | |||||
| 28 | Sewing on button lingerie single thread, chain stitch, without button shank (107) | 2 Hole | 7 | NT: 0.20m | 100% |
| 4 Hole | 14 | NT: 0.40m | 100% | ||
| 29 | Sewing on buttonOuter wear, single thread, chain stitch, with button shank (107) | 4 Hole | 21 | NT: 0.60m | 100% |
| 30 | Sewing on button, double lock stitch- zigzag (304) | 2 Hole | 6 | NT: 0.10m | 65% |
| BT: 0.05m | 35% | ||||
| 0.15m | |||||
| 4 Hole | 12 | NT: 0.10m | 65% | ||
| BT: 0.05m | 35% | ||||
| 0.15m |
Sewing Thread Consumption in the Apparel Industry:
Manufacturers can maximize material usage, cut waste, and guarantee constant product quality by comprehending and precisely calculating thread consumption. An outline of sewing thread consumption is provided here, along with information on practical issues, calculation techniques, and factors that influence it. Different apparel clothing consumption in the following:
Sewing Thread Consumption for Men’s and Boy’s Wear:
| Sewing Thread for Men’s and Boy’s Wear | |||||
| SL No. | Apparel Style | Standard Amount (m) | Range of Variation (m) | Distribution | |
| Over locking Seam (m) | Assembly & Ornamental Seam (m) | ||||
| 01 | Business suit trousers | 300 | 250-350 | 170 | 130 |
| 02 | Blue denim jeans | 280 | 230-370 | 130 | 150 |
| 03 | Sack coat, Blazer | 190 | 170-240 | 45 | 145 |
| 04 | Waist coat | 70 | 57-80 | – | 70 |
| 05 | Winter coat | 265 | 250-285 | 60 | 205 |
| 06 | Poplin coat | 265 | 250-285 | 40 | 225 |
| 07 | Shorts | 90 | 80-100 | 50 | 40 |
| 08 | Smock | 255 | 230-285 | 90 | 165 |
| 09 | Work suit (Two piece) | 375 | 345-400 | 185 | 190 |
| 10 | Bib slacks | 225 | 200-250 | 115 | 110 |
| 11 | Anorak, Blouson | 210 | 170-250 | 40 | 170 |
| 12 | Bathing, Dressing gown | 210 | 170-250 | 110 | 100 |
| 13 | Track suit | 200 | 170-250 | 120 | 80 |
| 14 | Men’s dress shirt (Long sleeved) | 125 | 115-150 | 80 | 45 |
| 15 | Men’s t-shirt | 80 | 70-90 | 65 | 15 |
Sewing Thread Consumption for Under Garments or Apparel:
| Sewing Thread for Under Garments or Apparel | |||||
| SL No. | Apparel Style | Standard Amount (m) | Range of Variation (m) | Distribution | |
| Over locking Seam (m) | Assembly & Ornamental Seam (m) | ||||
| 01 | Ladies panties | 100 | 80-100 | 80 | 80 |
| 02 | Men’s brief | 100 | 8-100 | 20 | 20 |
| 03 | Panty girdle | 100 | 80-120 | 80 | 20 |
| 04 | Bra | 55 | 40-80 | 20 | 35 |
| 05 | Pyjama | 200 | 170-200 | 120 | 80 |
| 06 | Night gown | 150 | 130-150 | 100 | 50 |
Sewing Thread Consumption for Ladies Wear:
| Sewing Thread for Ladies Wear | |||||
| SL No. | Apparel Style | Standard Amount (m) | Range of Variation (m) | Distribution | |
| Over locking Seam (m) | Assembly & Ornamental Seam (m) | ||||
| 01 | Dress (Unlined) | 150 | 125-180 | 90 | 60 |
| 02 | Dress Lined) | 195 | 160-255 | 100 | 95 |
| 03 | Skirt (Unlined) | 110 | 90-140 | 75 | 35 |
| 04 | Skirt Lined) | 170 | 150-200 | 125 | 45 |
| 05 | Jacket | 200 | 17-250 | 60 | 140 |
| 06 | Costume (Two piece) | 400 | 310-490 | 135 | 265 |
| 07 | Slacks | 200 | 180-240 | 150 | 50 |
| 08 | Poplin coat | 285 | 250-370 | 45 | 240 |
| 09 | Winter coat | 285 | 250-370 | 45 | 240 |
| 10 | Smock | 225 | 170-280 | 75 | 150 |
| 11 | Blouse | 120 | 100-150 | 55 | 65 |
| 12 | Bathing suit | 120 | 100-140 | 70 | 50 |
| 13 | Pyjama suit | 200 | 170-250 | 100 | 100 |
If you know the correct thread consumption, it will be easy to order and budget quantity against the buyer’s order. Above all ways to Calculate Sewing Thread Consumption would require in the garments industry.
- You may love to read: Types of Cost or Costing in Textile and Apparel Business
- How to Calculate Knitting Costs in the Textile Industry?
- How to Calculate Shipping and Forwarding Cost of Apparel Export Order?
- How to Calculate Fabric Consumption for Polo Shirt in Apparel Industry
- How to Calculate Printing Costs in the Apparel Industry?
- How to Calculate Stitching Costs in the Apparel Industry?
