Fabric Manufacturing Process: Woven, Nonwoven and Knit
The term fabric originated from the Latin word fabrica, meaning a “workshop. It means that which is put together like a building. Fabrics are textile surfaces; these structures are extremely long and wide in comparison with their thickness. It is based on the conversion of fiber or yarn into fabric consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibers. Fabrics are formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, braiding, or plaiting and bonding of fibers and pressing fibers together (felt). Wanna know about the fabric manufacturing process flow chart –
Flow Chart of Fabric Manufacturing Process:
These are all about the fabric manufacturing process flowchart. To be a little bit technical, we have to know about the process flow chart. So, we hope you will have a clear concept of this topic from this content.
Yarn from spinning section
↓
Doubling & Twisting
↓
Winding
↓
Warp yarn preparation Weft yarn preparation
↓ ↓
Cone winding For conventional loom (Shuttle loom) / For modern loom (Shuttleless loom)
↓ ↓
Crilling Pirn winding (for shuttle loom) / Cone winding (for shuttleless loom)
↓
Warping
↓
Sizing
↓
Winding on weaver’s beam
↓
Drawing
↓
Denting
↓
Looming
↓
Weaving
↓
Inspection of grey cloth
↓
Folding
↓
Packing
↓
Delivery
Fabric manufacturing process in textile engineering is the second step of textile processing. After collecting raw materials, this process starts. The raw materials for the fabric manufacturing process is yarn. Yarn and finishing chemicals are the raw materials for the fabric manufacturing process in textile engineering. It is the step-by-step process. Here, in every process, one has to be careful. There are different types of fabric in textile manufacturing. Woven, knit, sweater knit, denim, etc, are the different fabric types. Every fabric type has its own manufacturing method. And here, one method is completely different from the others. The raw materials used in fabric manufacturing process in textile engineering are also different. So there is no chance to discuss the whole process in same department.
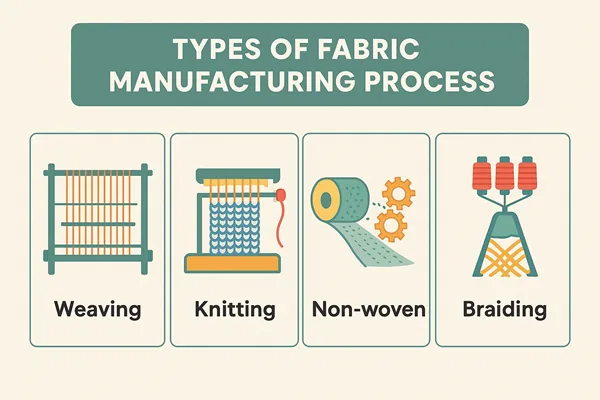
Fabric manufacturing process for different fabric types
- Woven
- Knit
- Sweater knit
- Nonwoven
1. Woven fabric manufacturing process
Woven fabric manufacturing processes in textile engineering are different from knit. Like that, knit fabric is different from sweater knit. Thereafter, it is closely similar to knit but not the same. Different fabrics have their own designs. So textile designers have to design first and then set up the repeating unit. After that, the process starts. There are basically four steps in the woven fabric procedure. Shedding, picking, beating and let off are the four steps.
2. Knit fabric manufacturing process
The knit fabric manufacturing process in textile engineering is different from the woven process. Its yarn type is also different. In knitting Cam set up is an important subject. The designer sets up Cam as the fabric design. Then the process starts. Different cams set different designs. Polo, Piqué, single jersey, Double jersey, etc are some came designs.
3. Sweater Knit fabric manufacturing process
Sweater has another manufacturing process. A sweater is another knitting process. It has some extra steps. For sweater knit, we use wool or cotton. Basically, we use wool. It is very comfortable to wear. The manufacturing reason for the sweater is only its warming power. People wear sweaters to warm themselves. So it is very important.
4. Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing Process
Nonwoven fabric is made by bonding or entangling fibers together without weaving or knitting. Fibers like polyester, polypropylene, or rayon are laid into a web through methods such as dry-laid, wet-laid, or spunbond processes. The web is then bonded using heat, chemicals, or mechanical techniques like needle punching or hydroentangling. This creates a fabric with specific properties suited for applications like medical textiles, filters, wipes, and geotextiles.
Conclusion
Woven, Nonwoven, Knit, and sweater are 4 different types of fabrics. All these have different types of processes in the fabric manufacturing, with different textures.
